[vc_row gap=”20″][vc_column css_animation=”fadeInLeft” width=”1/3″][ult_sticky_section sticky_gutter=”150″]
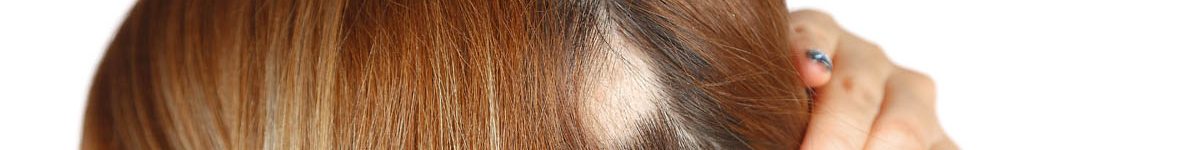
[vc_empty_space height=”10″][vc_empty_space height=”10px”]Treatments[vc_empty_space height=”10px”][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner offset=”vc_hidden-sm vc_hidden-xs”][vc_widget_sidebar show_bg=”false” sidebar_id=”sidebar_3″][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][/ult_sticky_section][/vc_column][vc_column width=”2/3″]Alopecia can be classified into different types based on the pattern and extent of hair loss. The most common types include androgenetic alopecia, alopecia areata, telogen effluvium, and traction alopecia. Androgenetic alopecia is a genetic condition that causes hair thinning and baldness in men and women. Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disorder that causes patchy hair loss on the scalp and other areas of the body. Telogen effluvium is a condition characterized by excessive shedding of hair due to stress, illness, medications, or hormonal changes. Traction alopecia is a type of hair loss caused by pulling or tension on the hair follicles, usually due to tight hairstyles.
The diagnosis of alopecia involves a thorough medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests to identify the underlying cause of hair loss. Treatment for alopecia depends on the type and severity of hair loss, as well as the underlying cause. Some common treatment options include medications such as topical minoxidil and oral finasteride, corticosteroid injections, hair transplant surgery, and scalp micropigmentation. In some cases, lifestyle modifications such as reducing stress and improving nutrition may also be helpful in managing hair loss. It is important to consult with a dermatologist or hair restoration specialist for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.[/vc_column_text][vc_row_inner el_id=”doctor-and-specialist”][vc_column_inner][vc_widget_sidebar show_bg=”false” sidebar_id=”sidebar_4″][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner]
In addition to dermatologists, primary care physicians, pediatricians, and gynecologists may also treat acne in their patients, particularly those with milder forms of the condition. However, for more severe cases or those that do not respond to initial treatments, a referral to a dermatologist may be necessary to ensure appropriate management of the condition. Patients with acne may also seek the advice of an esthetician, who can provide guidance on skin care routines and recommend over-the-counter products to help manage the condition.[/vc_cta][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][vc_row_inner el_id=”treatments”][vc_column_inner][vc_single_image image=”554″ img_size=”500×200″][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner]
Some individuals may also benefit from counseling or support groups to manage the emotional impact of hair loss. It is important to note that there is no cure for alopecia, and treatment aims to manage symptoms and slow or stop further hair loss. It is recommended to speak with a dermatologist or a hair specialist to determine the best course of treatment based on the type and severity of alopecia.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][/vc_column][/vc_row]